Understanding IT Service Management (ITSM)
IT Service Management (ITSM) is a systematic approach to designing, delivering, managing, and improving the way IT services are used within an organization. At its core, ITSM aims to align the delivery of IT services with the needs of the business, ensuring that the right processes, technology, and people are in place to support the business’s objectives and enhance user satisfaction.
One of the fundamental aspects of ITSM is the focus on processes. These are standardized and documented sets of activities designed to achieve specific objectives, such as incident management, change management, and problem management. These processes are often based on best practices and frameworks like ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library), which provides a structured approach to managing IT services efficiently and effectively.
Technology is another critical component of ITSM. It encompasses the tools and platforms that facilitate the management and delivery of IT services. These technologies enable automation, monitoring, and reporting, which are essential for maintaining high service levels and ensuring that IT services are always available and performing optimally. Examples of such technologies include service desk software, monitoring tools, and configuration management databases (CMDBs).
People are the third pillar of ITSM. This includes not only the IT staff who deliver and manage the services but also the end-users who rely on these services to perform their daily tasks. Effective ITSM requires a skilled and knowledgeable workforce that can handle the complexities of IT service delivery and possess a customer-centric mindset. Training and continuous development of IT personnel are crucial to maintaining high standards of service management.
In summary, IT Service Management is a holistic approach that integrates processes, technology, and people to deliver high-quality IT services aligned with business needs. By focusing on these critical components, organizations can ensure that their IT services are reliable, efficient, and capable of driving business success.
Explore Category: Business Services
Find Posts related to: IT Service Management
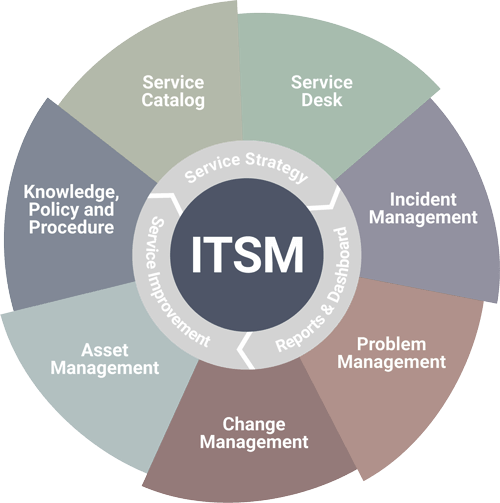
Table of Contents
The Origins of ITSM
The origins of IT Service Management (ITSM) can be traced back to the 1980s, a period marked by the rapid expansion of information technology within organizations. As businesses increasingly relied on IT systems to support their operations, the need for a structured approach to managing these services became apparent. Early efforts to formalize IT service processes were driven by the desire to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the quality of service delivery.
One of the pivotal moments in the history of ITSM was the development of the IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL) by the Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA) of the UK government. Initiated in the late 1980s, ITIL aimed to create a set of best practices for IT service management that could be adopted across different organizations. The first version of ITIL provided comprehensive guidelines on various aspects of IT service management, including service support, service delivery, and infrastructure management.
ITIL’s introduction marked a significant milestone in the evolution of ITSM. It offered a standardized framework that organizations could use to align their IT services with business needs. The framework emphasized the importance of processes, roles, and responsibilities in delivering high-quality IT services, thus laying the foundation for modern ITSM practices. Over the years, ITIL has undergone several revisions and updates, reflecting the changing landscape of IT and the growing complexity of service management.
In addition to ITIL, other frameworks and standards have contributed to the development of ITSM. For instance, the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) and ISO/IEC 20000 standards have provided additional guidance on process improvement and service management. These frameworks have collectively helped organizations to adopt a more systematic and disciplined approach to managing IT services.
The evolution of ITSM from its early beginnings to its current state underscores the importance of structured and standardized practices in managing IT services. By adopting frameworks like ITIL, organizations can ensure that their IT services are delivered efficiently and effectively, ultimately contributing to improved business outcomes.
The Evolution of ITSM
IT Service Management (ITSM) has undergone significant transformations since its inception. Initially, ITSM was characterized by manual processes and basic task management, primarily focused on maintaining and supporting IT infrastructure. Over the years, the field has evolved to embrace automation, cloud computing, and agile methodologies, each bringing about profound changes in how IT services are delivered and managed.
The early days of ITSM were marked by labor-intensive activities, where IT professionals manually handled tasks such as incident management, change control, and service requests. This manual approach was not only time-consuming but also prone to human error, which often led to inefficiencies and service disruptions. The advent of automation tools revolutionized ITSM by streamlining these processes, reducing the likelihood of errors, and improving overall service efficiency.
As businesses began to adopt cloud computing, ITSM frameworks had to adapt to the new paradigm. Cloud computing introduced a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective way to manage IT resources, but it also brought new challenges. ITSM practices were updated to include cloud service management, focusing on areas such as cloud resource provisioning, cost management, and security. This shift allowed organizations to leverage the benefits of cloud computing while maintaining robust IT service management practices.
The integration of agile methodologies further transformed ITSM by promoting a more iterative and collaborative approach to service management. Agile principles, such as continuous improvement and customer-centricity, became integral to ITSM frameworks. This shift enabled IT teams to respond more swiftly to changing business needs, deliver higher-quality services, and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
In response to these technological advancements and evolving business requirements, ITSM frameworks have been continually updated. Standards such as ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) have undergone multiple revisions to incorporate best practices for automation, cloud service management, and agile methodologies. These updates ensure that ITSM remains relevant and effective in addressing contemporary IT challenges.
Overall, the evolution of ITSM reflects a journey towards greater efficiency, adaptability, and alignment with business objectives. The ongoing updates to ITSM frameworks highlight the field’s commitment to embracing technological advancements and meeting the dynamic needs of modern organizations.
Key ITSM Frameworks and Standards
In the realm of IT Service Management (ITSM), several frameworks and standards provide the necessary guidance for organizations to implement effective service management practices. Among the most prominent are ITIL, COBIT, and ISO/IEC 20000. Each of these frameworks offers a structured approach to managing IT services, ensuring alignment with business objectives, and enhancing service quality.
ITIL
The Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) is perhaps the most widely recognized ITSM framework. ITIL provides a comprehensive set of best practices for managing IT services throughout their lifecycle, from initial planning to delivery and support. By adopting ITIL, organizations can standardize their service management processes, improve service delivery, and achieve greater efficiency. The framework is divided into five core stages: Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement. Each stage encompasses specific processes and activities aimed at delivering value to customers and stakeholders.
COBIT
Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies (COBIT) is another critical ITSM framework, developed by ISACA. While ITIL focuses on IT service management, COBIT provides a broader governance and management framework for enterprise IT. COBIT aligns IT goals with business objectives, ensuring that IT investments generate value and mitigate risks. The framework is built around five key principles: Meeting Stakeholder Needs, Covering the Enterprise End-to-End, Applying a Single Integrated Framework, Enabling a Holistic Approach, and Separating Governance from Management. COBIT helps organizations achieve effective IT governance and management by providing a comprehensive set of controls and practices.
ISO/IEC 20000
ISO/IEC 20000 is an international standard for IT service management. It defines the requirements for an organization’s ITSM system, ensuring that IT services are managed effectively and efficiently. The standard is based on the ITIL framework and provides a formal certification process, enabling organizations to demonstrate their commitment to quality IT service management. ISO/IEC 20000 covers aspects such as service delivery, relationship management, resolution processes, and control processes. Adhering to this standard helps organizations improve service quality, enhance customer satisfaction, and achieve operational excellence.
In addition to these primary frameworks, organizations may also consider other relevant standards and methodologies, such as Lean IT, Six Sigma, and DevOps. These approaches further complement ITSM practices, fostering continuous improvement, efficiency, and collaboration within IT teams.
Core Processes of ITSM
IT Service Management (ITSM) encompasses a range of core processes designed to ensure the efficient delivery and management of IT services within an organization. These processes are integral to maintaining operational stability, improving service quality, and aligning IT services with business objectives. Below, we delve into some of the fundamental processes that form the backbone of ITSM.
Incident Management
Incident Management aims to restore normal service operation as quickly as possible following an interruption or degradation. This process is pivotal in minimizing the impact of incidents on business operations. By promptly addressing incidents, organizations can maintain service levels and reduce downtime, thereby enhancing user satisfaction and productivity.
Problem Management
While incident management deals with immediate fixes, Problem Management focuses on identifying and mitigating the root causes of incidents. This proactive approach helps prevent incidents from recurring. Effective problem management involves thorough root cause analysis, implementing permanent solutions, and maintaining a known error database to streamline future issue resolution.
Change Management
Change Management is critical for controlling the lifecycle of all changes to IT services. Its goal is to ensure that beneficial changes are implemented with minimal disruption to existing services. This process involves evaluating, authorizing, and documenting changes, thus mitigating risks associated with service alterations. A well-structured change management process can significantly enhance service reliability and business agility.
Service Request Management
Service Request Management handles user requests for service enhancements, information, or access to IT resources. This process ensures that service requests are efficiently managed and fulfilled in accordance with predefined service level agreements (SLAs). By streamlining request handling, organizations can improve response times and user satisfaction.
Additional ITSM Processes
Beyond the aforementioned processes, ITSM also includes other essential processes such as Configuration Management, which maintains an accurate record of IT assets and their relationships, and Release Management, which oversees the deployment of new or modified services. Capacity Management ensures that IT resources are adequately scaled to meet current and future demands, while Service Level Management monitors and reports on service performance against agreed-upon SLAs.
Together, these core processes of ITSM form a cohesive framework that enables organizations to deliver high-quality IT services, optimize resource utilization, and align IT initiatives with business objectives. By implementing and continuously improving these processes, businesses can achieve greater operational efficiency and drive sustainable growth.
The Role of ITSM Tools and Technology
In the evolving landscape of IT Service Management (ITSM), tools and technology play a pivotal role in enabling organizations to streamline their IT processes and enhance service delivery. Modern ITSM tools are integral to implementing and maintaining effective ITSM practices, providing a comprehensive platform for managing IT services, incidents, problems, changes, and more. Among the popular ITSM software solutions, ServiceNow and BMC Remedy stand out due to their robust features and functionalities.
ServiceNow offers a cloud-based platform that integrates IT service management with other business processes, delivering a unified approach to IT operations. Key features of ServiceNow include incident management, change management, problem management, and service catalog. The platform also boasts advanced capabilities such as automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML), which help in predicting issues before they arise and automating routine tasks. These functionalities enable organizations to reduce downtime, improve service quality, and enhance customer satisfaction.
BMC Remedy, on the other hand, is known for its powerful ITSM suite that supports end-to-end IT service management. Remedy’s features include comprehensive incident and problem management, change and release management, and asset management. The platform’s flexibility allows for extensive customization to meet the specific needs of an organization. Additionally, BMC Remedy includes cognitive capabilities that leverage AI for better decision-making and efficiency. This tool is designed to provide a seamless experience, ensuring that IT services are delivered effectively and aligned with business objectives.
Other notable ITSM tools include Cherwell, Ivanti, and Jira Service Management. Each of these tools offers unique capabilities tailored to different organizational needs. Cherwell is known for its ease of use and quick deployment, Ivanti for its robust security features, and Jira Service Management for its integration with agile project management practices. These tools collectively provide a suite of functionalities that support the entire IT service lifecycle, from service request management to performance analytics.
In essence, the adoption of ITSM tools and technology is critical for organizations aiming to enhance their IT service delivery. These tools not only streamline processes and improve efficiency but also ensure that IT services are aligned with business goals, ultimately driving organizational success.
Benefits of ITSM for Businesses
IT Service Management (ITSM) offers numerous benefits that can significantly enhance the operations of any business. One of the primary advantages is the improvement in service quality. By adopting ITSM frameworks, organizations can establish standardized processes that ensure consistency and reliability in service delivery. This standardization minimizes errors and increases the overall quality of IT services provided to internal and external customers.
Another critical benefit is the increase in operational efficiency. ITSM practices streamline IT operations through well-defined workflows and automation of repetitive tasks. This not only speeds up service delivery but also frees up valuable IT resources to focus on more strategic initiatives. As a result, businesses can achieve higher productivity and better resource utilization.
Cost reduction is also a notable benefit of ITSM. By optimizing processes and eliminating inefficiencies, businesses can reduce operational costs. Effective incident and problem management minimize downtime and prevent costly disruptions. Additionally, ITSM’s proactive approach to maintenance and support helps in avoiding unexpected expenses related to IT failures and outages.
Enhancing customer satisfaction is another significant advantage. ITSM frameworks prioritize customer-centric service delivery, ensuring that IT services meet or exceed customer expectations. Through effective service level management and continuous improvement processes, businesses can enhance their responsiveness to customer needs, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
Strategically, implementing ITSM provides a better alignment of IT services with business goals. ITSM practices ensure that IT initiatives support the overall objectives of the organization, enabling a more cohesive and integrated approach to achieving business outcomes. Moreover, ITSM helps businesses comply with regulatory requirements by establishing governance and control mechanisms that ensure adherence to relevant standards and policies.
In summary, ITSM offers a comprehensive set of benefits that can transform how businesses manage their IT services. Improved service quality, increased efficiency, cost reduction, enhanced customer satisfaction, and strategic alignment are just a few of the key advantages that make ITSM an invaluable asset for any organization.
Future Trends in ITSM
As the landscape of IT service management (ITSM) continues to evolve, several emerging trends and technologies are poised to redefine the field. One of the most significant advancements is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). These technologies are enhancing the capacity for automated incident management, predictive analytics, and more efficient resource allocation. AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants are increasingly being deployed to handle routine service desk tasks, reducing the workload on human agents and improving response times.
Machine learning algorithms are also being utilized to analyze vast amounts of data, uncovering patterns and insights that can drive proactive problem management. By predicting potential system failures and identifying areas for improvement, ML algorithms help organizations maintain higher levels of service availability and performance. This proactive approach not only minimizes downtime but also enhances overall customer satisfaction.
Another critical trend shaping the future of ITSM is the heightened focus on cybersecurity. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, IT service management practices must evolve to include robust security measures. Integrating cybersecurity protocols within ITSM frameworks ensures that organizations can swiftly respond to and mitigate security incidents. This integration also facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements, thereby safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining trust with stakeholders.
Additionally, the convergence of ITSM with DevOps practices is gaining traction. This integration fosters a more collaborative environment between development and operations teams, leading to faster deployment of services and applications. By breaking down silos and promoting continuous feedback loops, organizations can achieve greater agility and more efficient service delivery.
Looking ahead, the ongoing evolution of ITSM will likely be influenced by these trends, driving organizations to adopt more innovative and adaptive approaches. Embracing AI, machine learning, and cybersecurity within ITSM frameworks will not only enhance operational efficiency but also ensure that IT services remain resilient and aligned with business objectives in an increasingly complex digital landscape.