Introduction to Renewable Energy
Combatting Climate Change
The Importance of Renewable Energy in Combatting Climate Change. Renewable energy refers to energy derived from natural sources that are replenished at a faster rate than they are consumed. Unlike non-renewable energy sources such as fossil fuels, which take millions of years to form and are finite, renewable energy sources are sustainable and have a lesser environmental impact. Key types of renewable energy include solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, each harnessing natural processes to generate electricity and other forms of power.
Solar energy captures sunlight using photovoltaic cells or solar thermal systems, converting it into electricity or heat. Wind energy exploits the kinetic energy from wind currents, using turbines to produce electricity. Hydroelectric power, on the other hand, utilizes the flow of water in rivers or dams to generate electrical energy. These renewable sources are crucial in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the adverse effects of climate change.
In recent years, there has been a growing global awareness of the urgent need to shift from fossil fuels to renewable energy. This shift is driven by the increasing recognition of climate change as a significant threat to the environment, human health, and the global economy. Governments, corporations, and individuals are increasingly adopting renewable energy solutions to decrease dependency on non-renewable resources, reduce carbon footprints, and promote sustainable development.
The adoption of renewable energy is supported by technological advancements, policy frameworks, and economic incentives that make it more accessible and cost-effective. As the world continues to grapple with the challenges posed by climate change, the transition to renewable energy remains a critical strategy in achieving a sustainable and resilient future.
Explore Category: Environmental Solutions
The Importance of Renewable Energy
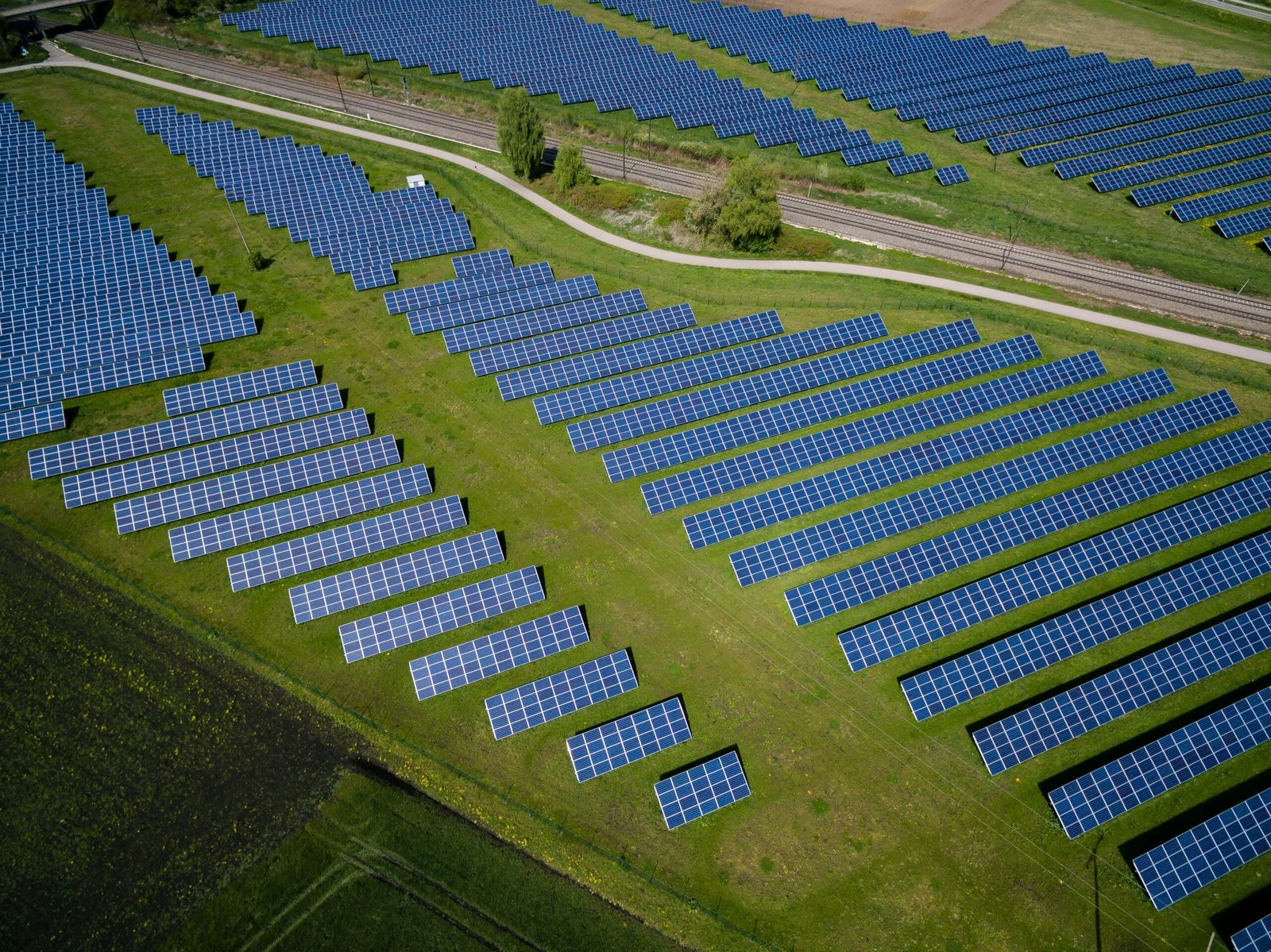

Table of Contents
The Role of Solar Energy
Solar energy stands as a pivotal player in the global shift towards renewable energy sources. Harnessing the power of the sun, solar panels convert sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic cells. This process, known as the photovoltaic effect, involves the absorption of photons from sunlight, which then dislodge electrons within the cells, creating an electric current. This conversion is not only efficient but also sustainable, as it relies on an inexhaustible natural resource: sunlight.
One of the most significant advantages of solar energy is its abundance. The sun emits enough energy in one hour to meet the world’s energy demands for an entire year. This sheer magnitude of available solar power underscores its potential as a cornerstone in the fight against climate change. Furthermore, the cost of solar technology has been steadily decreasing, making it more accessible to a broader audience. Advances in technology and increased production have driven down the price of solar panels, making it a viable option for both residential and commercial applications.
Solar energy’s impact on reducing greenhouse gas emissions is profound. Unlike fossil fuels, solar power generation does not release harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. By replacing traditional energy sources with solar energy, we can significantly cut down carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases, which are major contributors to global warming. This transition not only mitigates environmental damage but also promotes public health by reducing air pollution.
Residential solar installations allow homeowners to generate their own electricity, reducing dependence on the grid and lowering utility bills. Additionally, commercial applications of solar energy are gaining traction, with businesses adopting solar power to cut operational costs and enhance their sustainability profiles. Large-scale solar farms are also being developed, contributing to the grid and supporting a broader renewable energy infrastructure.
In essence, solar energy offers a versatile and impactful solution to combat climate change. Its abundant nature, coupled with decreasing costs and significant environmental benefits, positions it as a key player in the transition towards a more sustainable and resilient energy future.
Harnessing the Power of Wind Energy
Wind energy stands at the forefront of renewable energy sources, playing a pivotal role in the global effort to combat climate change. The principle behind wind energy is relatively straightforward: wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of wind into mechanical power, which is then transformed into electricity through a generator. This method of electricity generation is both efficient and sustainable, leveraging a natural resource that is abundant and inexhaustible.
One of the primary advantages of wind energy is its ability to provide electricity at very low operational costs. Once the wind turbines are installed and operational, the cost of maintaining and running them is minimal compared to traditional fossil fuel-based power plants. Moreover, wind energy is scalable; it is suitable for small-scale installations, such as individual turbines providing power to a single household, as well as large-scale wind farms capable of generating electricity for thousands of homes and businesses.
Wind farms can be located both onshore and offshore, each with its unique benefits. Onshore wind farms are typically easier and less expensive to install and maintain. They can be integrated into existing agricultural or rural landscapes with minimal disruption. Offshore wind farms, on the other hand, tap into the stronger and more consistent wind patterns found over bodies of water, resulting in higher energy output. Additionally, offshore installations often encounter fewer obstacles and opposition compared to onshore projects, as they are typically situated away from populated areas.
The role of wind energy in reducing carbon footprints cannot be overstated. By substituting fossil fuel-based power generation with wind energy, we significantly cut down on greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a cleaner, healthier environment. Furthermore, wind energy fosters energy sustainability by diversifying the energy mix and reducing dependence on non-renewable resources. This transition is crucial for achieving long-term environmental goals and ensuring a stable and resilient energy infrastructure for future generations.
The Significance of Hydroelectric Power
Hydroelectric power is a vital component in the global effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. This renewable energy source harnesses the kinetic energy of flowing water to generate electricity. The process typically involves the construction of a dam on a river, which creates a reservoir or a diverted water flow system. Water released from the reservoir flows through turbines, spinning them, and activating generators to produce electricity. The generated electricity is then transmitted to homes and businesses, providing a reliable and continuous power supply.
One of the most significant environmental benefits of hydroelectric power is its minimal production of greenhouse gases. Unlike fossil fuels, hydroelectric plants do not burn fuel, resulting in substantially lower carbon dioxide and methane emissions. This reduction in greenhouse gases is crucial in the fight against climate change, as it helps to mitigate global warming and its associated adverse effects on the environment.
In addition to its environmental benefits, hydroelectric power is known for its reliability and efficiency. Hydropower plants can quickly adjust to fluctuations in electricity demand, ensuring a stable and consistent energy supply. This reliability is particularly beneficial during peak usage times or in emergency situations when additional power is required. Furthermore, the operational costs of hydroelectric plants are relatively low compared to fossil fuel-based power plants, making it an economically viable option for many regions.
However, while hydroelectric power is largely beneficial, it can have potential ecological impacts. The construction of dams and reservoirs can alter natural water flows, affecting aquatic ecosystems and the species that depend on them. Potential mitigation measures include the implementation of fish ladders and bypass systems, which allow fish to navigate around dams, and the careful management of water releases to mimic natural flow patterns. By incorporating these strategies, the ecological impacts of hydroelectric power can be significantly reduced.
In summary, hydroelectric power is a crucial renewable energy source that offers substantial environmental and economic benefits. By understanding and addressing its potential ecological impacts, we can continue to harness this reliable and efficient energy source in a sustainable manner.
Comparative Analysis of Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, each offer unique advantages and limitations. A comprehensive understanding of these attributes is crucial for developing a balanced and resilient energy grid capable of addressing climate change.
Solar Power: Solar energy harnesses sunlight through photovoltaic cells or solar thermal systems. Its primary strength lies in its vast availability and the rapid decline in associated costs. Technological advancements have significantly improved the efficiency of solar panels, making solar power increasingly cost-effective. However, solar energy’s effectiveness is contingent on geographic location and weather conditions. Areas with high solar irradiance, such as deserts, are ideal, while regions with prolonged cloudy periods may find solar less reliable.
Wind Power: Wind energy is captured using turbines that convert kinetic energy from wind into electricity. Wind power is highly efficient in regions with consistent and strong wind patterns, such as coastal areas and open plains. The cost of wind energy has also decreased, making it competitive with traditional fossil fuels. However, wind power faces challenges, including intermittency and the need for substantial land use. Additionally, some regions may not have the necessary wind resources to justify large-scale wind farms.
Hydroelectric Power: Hydroelectric energy generates power by using the flow of water to turn turbines. It is a highly reliable and efficient source of renewable energy, especially in regions with significant water resources. Hydroelectric plants can provide consistent base-load power and have low operational costs once established. However, the construction of dams and reservoirs can have significant environmental and social impacts, including habitat disruption and displacement of local communities. Moreover, hydroelectric potential is limited to regions with suitable hydrological conditions.
Integrating a mix of these renewable energy sources can create a balanced and resilient energy grid. The complementary nature of solar, wind, and hydroelectric power can mitigate the intermittency issues associated with individual sources. For instance, solar power is abundant during sunny days, while wind power can be harnessed during windy nights. Hydroelectric plants can provide stability and act as a buffer during periods of low solar and wind output. By leveraging the strengths of each renewable energy source, it is possible to develop a more sustainable and reliable energy infrastructure capable of significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Technological Advancements and Innovations
Recent technological advancements in renewable energy have significantly contributed to the global effort to combat climate change. One notable area of progress is in solar panel technology. Modern solar panels have achieved higher efficiency rates through the use of advanced materials and innovative manufacturing techniques. These improvements allow for greater energy capture from sunlight, making solar power a more viable and cost-effective option for both residential and commercial use.
Wind energy has also seen remarkable advancements, particularly in wind turbine design. Enhanced aerodynamics, longer blades, and more efficient generators have increased the energy output of wind turbines. Additionally, offshore wind farms are becoming more prevalent due to their ability to harness stronger and more consistent winds, further boosting the overall capacity of wind energy production.
Hydroelectric power generation has benefitted from innovative methods that improve efficiency and minimize environmental impact. For instance, new turbine designs and advanced control systems are optimizing the performance of hydroelectric plants, while “run-of-river” systems provide a more sustainable alternative by reducing the need for large reservoirs and dams.
Emerging technologies are also playing a crucial role in enhancing the integration of renewable energy into existing infrastructure. Energy storage solutions, such as advanced battery technologies, are essential for addressing the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources. These storage systems enable the capture and retention of excess energy generated during peak production times, which can then be utilized during periods of low generation.
Smart grids represent another significant innovation in the renewable energy sector. These intelligent systems facilitate real-time monitoring and management of energy distribution, ensuring a more efficient and reliable integration of renewable sources. Smart grids can dynamically adjust to fluctuations in energy supply and demand, thereby enhancing the stability and resilience of the overall energy network.
Through these technological advancements and innovations, renewable energy is becoming increasingly capable of meeting global energy needs while reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Policy and Economic Implications
The adoption of renewable energy is significantly influenced by various policy measures and economic incentives. Governments worldwide have recognized the pivotal role that renewable energy plays in mitigating climate change and have accordingly devised a range of supportive policies. These include government subsidies and tax credits aimed at reducing the financial burden on renewable energy projects and making them more competitive with traditional fossil fuels.
Government subsidies are a critical tool in this context. By offering financial support to renewable energy projects, these subsidies lower the initial capital costs, making it more feasible for companies to invest in technologies like solar and wind power. Additionally, tax credits serve as an economic incentive by allowing businesses and homeowners to deduct a portion of the expenses incurred from their taxable income, further encouraging the shift toward renewable energy sources.
International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, also play a crucial role in promoting the adoption of renewable energy. This landmark agreement has seen nations commit to reducing their carbon emissions and investing in sustainable energy solutions. By setting ambitious targets and fostering global cooperation, the Paris Agreement serves as a powerful catalyst for renewable energy development.
From an economic perspective, the transition to renewable energy offers several benefits. One of the most significant is job creation. The renewable energy sector has been a major driver of employment growth, providing jobs in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and more. This not only boosts local economies but also helps to address unemployment issues in various regions.
Energy independence is another vital economic benefit. By investing in renewable energy, countries can reduce their reliance on imported fossil fuels, enhancing national security and economic stability. This shift not only helps to stabilize energy prices but also shields economies from the volatility of global oil and gas markets.
Future Outlook and Challenges
The future of renewable energy holds immense promise, but it is not without its challenges. As the global community increasingly recognizes the urgency of addressing climate change, the shift towards renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power is accelerating. Anticipated trends indicate a significant rise in the adoption of these technologies, driven by falling costs, advancements in energy storage, and improved grid integration.
However, several obstacles remain on the path to a fully renewable energy landscape. One major challenge is the intermittency of renewable energy sources. Solar and wind power, for instance, are dependent on weather conditions and time of day, which can lead to fluctuations in energy supply. Advanced energy storage solutions and smart grid technologies are crucial to mitigating these issues, ensuring a reliable and consistent energy supply.
Another significant challenge lies in the existing infrastructure. Transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy requires substantial upgrades to current energy systems, which can be both time-consuming and costly. Investments in modernizing the grid, enhancing transmission capabilities, and developing more efficient energy storage systems are essential to support the growing share of renewables in the energy mix.
Policy support and international cooperation play a pivotal role in overcoming these challenges. Governments must establish favorable policies, incentives, and regulations to encourage the adoption of renewable energy. This includes implementing carbon pricing mechanisms, offering subsidies for renewable energy projects, and setting ambitious renewable energy targets. Additionally, international collaboration is vital to share best practices, facilitate technology transfer, and mobilize financial resources.
Continued innovation is another key factor in the renewable energy future. Research and development efforts must focus on improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of renewable technologies, as well as exploring new avenues for harnessing clean energy. Breakthroughs in areas such as advanced materials, artificial intelligence, and biotechnology could further revolutionize the renewable energy sector.
In the battle against climate change, transitioning to renewable energy is not just an option but a necessity. By addressing the challenges and capitalizing on the opportunities, the global community can pave the way for a sustainable and resilient energy future, ultimately safeguarding the planet for generations to come.