Administrators managing Office 2021 and Office 2024 often struggle to understand how security updates are delivered in modern Microsoft-managed environments. There are no visible patch downloads, update pages reference Click-to-Run, and neither Intune nor Windows Autopatch shows Office CVEs as deployable updates. This leads to uncertainty during security incidents and audits.
This article explains how Office updates actually work when devices are managed by Microsoft Intune and Windows Autopatch, and how administrators should validate that Office is fully patched.
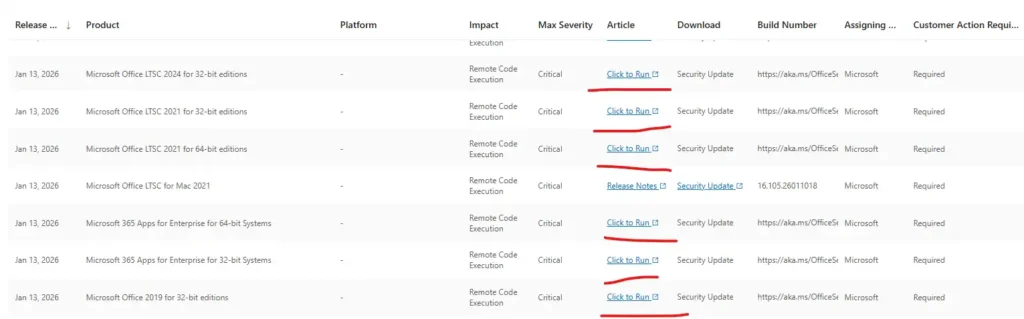
This post was written in addition to: CVE-2026-20952 updates and avoid confusion for most of the Admins to understand what needs to be done to mitigate vulnerabilities.
Explore more in Microsoft 365 section.
How Office Updates Work with Intune and Autopatch

Modern Office Servicing Model Overview
All supported perpetual Office versions today use the Click-to-Run (C2R) servicing model.
This includes:
- Office 2021
- Office 2024
- Office LTSC 2021
- Office LTSC 2024
Click-to-Run is not an installation option and not a download method. It is the servicing architecture that defines how Office binaries are updated and maintained.
Key characteristics of Click-to-Run:
- No MSI installers
- No standalone patch files
- No individual KB packages
- Updates are delivered as new Office builds
Office 2024 vs Office LTSC 2024 (Servicing Clarification)
A common misunderstanding is the belief that Office 2024 and Office LTSC 2024 are different in how they receive updates.
In reality:
- Office 2024 is the product name
- LTSC 2024 is the servicing channel
All Office 2024 perpetual editions (Standard, Professional, etc.):
- Use LTSC 2024 servicing
- Receive security updates only
- Share the same update history and build numbers
When Microsoft documentation or security advisories reference Office LTSC 2024, they apply directly to Office 2024 suites.
Why There Is No “Patch Download” Option
Microsoft Office Click-to-Run updates are build-based, not file-based.
When an update is released:
- Microsoft publishes a new Office build to Microsoft Update
- Devices compare their installed build with the latest available build
- Only changed binaries are downloaded
- Office updates silently in the background
Because updates are incremental binary changes:
- There is no downloadable patch file
- There is no update catalog entry
- There is no manual install option
Update history pages are informational, not deployment portals.
The Role of Microsoft Intune
Microsoft Intune does not deploy Office updates directly.
Intune’s responsibility is to control whether devices are allowed to receive Office updates.
The most critical setting is found in:
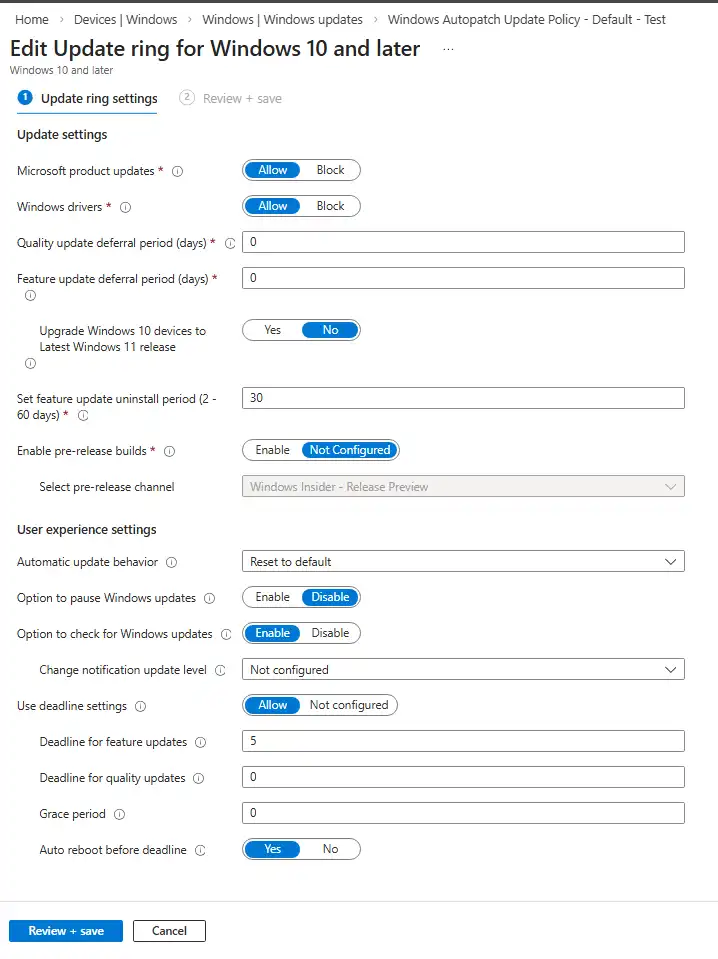
Devices → Windows → Update rings for Windows 10 and later
Required configuration:
- Receive updates for other Microsoft products = Enabled
This setting allows devices to contact Microsoft Update instead of Windows Update only.
If this setting is disabled:
- Windows OS updates still install
- Office does not receive security updates
- Office CVEs remain unpatched without visible errors
Office “Automatic Updates” inside the app cannot override this restriction.
How Windows Autopatch Changes Update Management
Organizations using Windows Autopatch sometimes believe they no longer use Windows Update. This is incorrect.
Windows Autopatch:
- Is built on Windows Update for Business
- Uses Microsoft Update
- Manages update rings, deferrals, and health automatically
- Replaces manual update administration, not the update infrastructure
For Office:
- Autopatch controls when updates install
- Microsoft Update controls what updates are delivered
- Office security fixes follow the same managed rollout
There is no separate Office update workflow under Autopatch.
What Windows Autopatch Manages (and What It Does Not)
Windows Autopatch does not manage all Microsoft products in the same way. Understanding its scope is essential to avoid confusion when validating update and CVE remediation, especially for Microsoft Office.
What Windows Autopatch Explicitly Manages
Windows Autopatch actively creates and manages policies for the following workloads:
- Windows quality updates
Monthly security and cumulative updates for the Windows operating system. - Windows feature updates
Controlled rollout of Windows version upgrades (where enabled). - Microsoft 365 Apps updates
Subscription-based Office (Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise), including:- Channel management
- Feature and security updates
- Microsoft Edge updates
Browser updates and security fixes.
For these workloads, Autopatch provides:
- Dedicated update controls
- Rollout rings
- Health monitoring
- Explicit visibility in the Autopatch UI
At this point, it is important to clearly separate what Windows Autopatch explicitly manages from products that are updated implicitly through Microsoft Update.
What Windows Autopatch Does Not Explicitly Manage
Windows Autopatch does not create a dedicated workload or toggle for:
- Office 2021 (Perpetual)
- Office 2024 (Perpetual)
- Office LTSC 2021 / Office LTSC 2024
- Office CVE-specific deployments
- Office patch downloads or KB approvals
These Office versions do not appear as selectable update types in the Autopatch UI.
This is expected behavior, not a configuration gap.
Why Office 2021 and Office 2024 Still Receive Updates
Office 2021 and Office 2024 use the Click-to-Run LTSC servicing model and are updated via Microsoft Update, not via an Autopatch-managed “app” workload.
Their update flow is:
- Microsoft Update eligibility
Enabled through the Windows Update ring setting:
Microsoft product updates = Allow - Windows Update for Business
Governs update availability and compliance. - Windows Autopatch deployment rings
Control rollout timing, deferrals, deadlines, and health. - Office Click-to-Run service
Installs the updated Office build silently on the device.
As a result, Office 2021 and Office 2024 updates are implicit, not explicit:
- They are allowed by Windows Update policy
- Timed by Autopatch
- Installed by the Office servicing engine
No separate Autopatch configuration is required.
Key Takeaway
Windows Autopatch explicitly manages Windows, Microsoft 365 Apps, and Edge.
Office 2021 and Office 2024 are updated implicitly via Microsoft Update, with rollout timing governed by Autopatch.
If these settings are enabled, Office security updates are delivered automatically.
Office 2021 and Office 2024 receive security updates via Microsoft Update using Windows Update for Business, with rollout timing managed by Windows Autopatch. No separate Office patch deployment is required.
How Office Security Fixes and CVEs Are Delivered
When Microsoft fixes an Office vulnerability:
- The fix is bundled into a new Office build
- The build is released to Microsoft Update
- Devices install it automatically if updates are allowed
There is:
- No CVE-specific package
- No approval step in Intune
- No Office CVE visibility in Autopatch
This is expected behavior.
How Microsoft Defines “Patched” for Office
Microsoft defines Office patching status only by Version and Build number.
This applies to:
- Office 2021
- Office 2024
- Office LTSC editions
Supported verification method:
- Open Word
- Go to File → Account
- Note:
- Version
- Build number
- Compare with the latest build listed in:
- Update history for Office 2021
- Update history for Office LTSC 2024
If the installed build is equal to or newer, the device is patched.
This is the method used by:
- Microsoft Support
- Security response teams
- Auditors
Common Misconceptions That Cause Confusion
- “We don’t see Office patches in Intune”
→ Intune does not deploy Office patches. - “Click-to-Run means we need to download something”
→ Click-to-Run is a servicing model. - “We don’t use LTSC”
→ Office 2024 uses LTSC servicing. - “Autopatch replaces Windows Update”
→ Autopatch is Windows Update for Business. - “Automatic updates guarantee immediate patching”
→ Update timing is controlled by rings and deferrals.
Operational Best Practices for Admins
To ensure Office remains secure:
- Confirm devices are enrolled in Windows Autopatch
- Verify Receive updates for other Microsoft products is enabled
- Avoid pausing quality updates during security incidents
- Validate Office builds on a sample of devices
- Keep update history references for audit evidence
Security and Compliance Impact
Misunderstanding Office servicing leads to:
- False vulnerability findings
- Delayed incident response
- Incorrect audit conclusions
Understanding that Office security equals build compliance allows organizations to respond confidently to zero-day vulnerabilities without unnecessary remediation efforts.
Conclusion
Office 2021 and Office 2024 updates are automatic, silent, and build-based. When managed through Intune and Windows Autopatch, there is no manual patching process and no visible downloads. Security validation depends entirely on allowing Microsoft Update and verifying Office build numbers.
Once this model is understood, Office patching becomes predictable, auditable, and reliable.